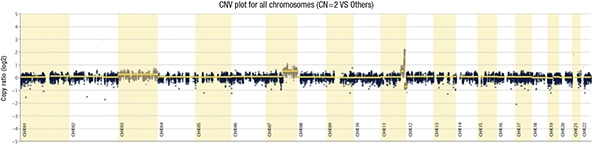
Fig. 5. Copy number variation was assessed using CNVkit software.
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2016;127(20):2375–2390.
- Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 3rd ed. Vol 3. IARC Press; 2001.
- Pienkowska-Grela B, Rymkiewicz G, Grygalewicz B, et al. Partial trisomy 11, dup(11)(q23q13), as a defect characterizing lymphomas with Burkitt pathomorphology without MYC gene rearrangement. Med Oncol. 2011;28(4):1589–1595.
- Salaverria I, Martin-Guerrero I, Wagener R, et al. A recurrent 11q aberration pattern characterizes a subset of MYC-negative high-grade B-cell lymphomas resembling Burkitt lymphoma. Blood. 2014;123(8):1187–1198.
- Aukema SM, Theil L, Rohde M, et al. Sequential karyotyping in Burkitt lymphoma reveals a linear clonal evolution with increase in karyotype complexity and a high frequency of recurrent secondary aberrations. Br J Haematol. 2015;170(6):814–825.
- Ferreiro JF, Morscio J, Dierickx D, et al. Post-transplant molecularly defined Burkitt lymphomas are frequently MYC-negative and characterized by the 11q-gain/loss pattern. Haematologica. 2015;100(7):e275–e279.
- Gonzalez-Farre B, Ramis-Zaldivar JE, Salmeron-Villalobos J, et al. Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration: a germinal center-derived lymphoma genetically unrelated to Burkitt lymphoma. Haematologica. 2019;104(9):1822–1829.
- Morin RD, Johnson NA, Severson TM, et al. Somatic mutations altering EZH2 (Tyr641) in follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of germinal-center origin. Nat Genet. 2010;42(2):181–185.
- Zhang J, Dominguez-Sola D, Hussein S, et al. Disruption of KMT2D perturbs germinal center B cell development and promotes lymphomagenesis. Nat Med. 2015;21(10):1190–1198.
- McCabe MT, Ott HM, Ganji G, et al. EZH2 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for lymphoma with EZH2-activating mutations. Nature. 2012;492(7427):108–112.
- Højfeldt JW, Agger K, Helin K. Histone lysine demethylases as targets for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(12):917–930.
Dr. Xu is a resident, Dr. Alsuwaidan was at the time of writing a hematopathology fellow, and Dr. Chen is an associate professor—all in the Department of Pathology, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas. Dr. Alsuwaidan is currently practicing in the Department of Pathology, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Saudi Arabia.
Test yourself
- Here are three questions taken from the case report.
- Answers
a. It refers to a subset of lymphomas that resemble Burkitt lymphoma but lack MYC translocation.
b. It has a chromosome 11q alteration characterized by proximal gains and telomeric losses.
c. It usually harbors complex karyotype.
d. All of the above
2. What types of cells are Burkitt lymphoma and Burkitt-like lymphoma derived from?
a. Mature B cells of unknown type
b. Pre-germinal center B cells
c. Germinal center B cells
d. Post-germinal center B cells
3. Which of the following ancillary techniques can be used in the diagnosis of Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration?
a. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
b. Array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH)
c. Next-generation sequencing
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
Answers are also online now at www.amp.org/casereports.
1. Which of the following statements is true regarding Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration?
a. It refers to a subset of lymphomas that resemble Burkitt lymphoma but lack MYC translocation.
b. It has a chromosome 11q alteration characterized by proximal gains and telomeric losses.
c. It usually harbors complex karyotype.
d. All of the above
2. What types of cells are Burkitt lymphoma and Burkitt-like lymphoma derived from?
a. Mature B cells of unknown type
b. Pre-germinal center B cells
c. Germinal center B cells
d. Post-germinal center B cells
3. Which of the following ancillary techniques can be used in the diagnosis of Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration?
a. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
b. Array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH)
c. Next-generation sequencing
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
 CAP TODAY Pathology/Laboratory Medicine/Laboratory Management
CAP TODAY Pathology/Laboratory Medicine/Laboratory Management
